Wood and forest products have long been appreciated as a versatile and sustainable material. But recent innovations are pushing the boundaries of its potential even further. Researchers around the globe are exploring new and exciting applications for wood and wood products, underscoring its role not just as a traditional building material but as a key resource in the future of sustainable technology and alternative fuels. From renewable energy sources to innovative construction materials and even space exploration, wood is proving to be a remarkably multipurpose and adaptable resource.
One of the primary reasons wood is so valuable in modern research is its sustainability. Sourced from responsibly managed forests, wood is a renewable resource that can be harvested and replanted, ensuring a continual supply for society. This cyclical nature not only supports forest health but also contributes to reducing our carbon footprint and addressing climate change.
Wood is a carbon-friendly material with carbon consisting half of its weight. And unlike steel, concrete and plastic, wood requires less energy to produce, resulting in lower carbon emissions.

Low-quality or otherwise unsellable wood is converted into renewable fuels that can heat homes and power vehicles.
Biofuel
The push for renewable energy has led researchers to explore wood’s potential as a source of biomass energy. There’s an abundance of low-quality, diseased trees or otherwise unsellable wood when thinning forested lands to reduce the severity of wildfires. Instead of allowing the wood material to go to waste, it can be converted into wood pellets, a renewable energy source.
Additionally, start-ups are looking to convert waste wood into sustainable aviation fuel with the potential to make biofuel production cost-effective and carbon neutral. A US Department of Energy analysis found that America could “sustainably triple its production of biomass…to satisfy future demand for clean aviation biofuel” and “fully decarbonize the entire domestic aviation industry with sustainable aviation fuel by 2050.”
Innovations like jet fuel and pellets made from timber byproducts not only utilize wood that would otherwise be wasted but also provide a cleaner, sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
Construction materials
Wood is increasingly recognized for its strength and versatility in construction. Mass timber products like cross-laminated timber (CLT) and glulam have revolutionized building designs. A notable innovation is Kerto LVL (Laminated Veneer Lumber), which boasts a strength-to-weight ratio similar to steel. This product enables the construction of load-bearing structures with less material, resulting in lighter buildings with reduced carbon emissions.

Transparent wood can be used for smartphone screens, light fixtures and windows.
Transparent wood
One of the most exciting innovations is the development of transparent wood, which is stronger than plastic and ten times tougher than glass. This material could potentially replace non-renewable materials in various applications. Researchers envision transparent wood being used for smartphone screens, glowing light fixtures, and even color-changing windows. The modification of wood into such high-performance materials emphasizes its potential to contribute to a carbon-neutral future.
Wooden satellites
Even space exploration is finding a place for wood.
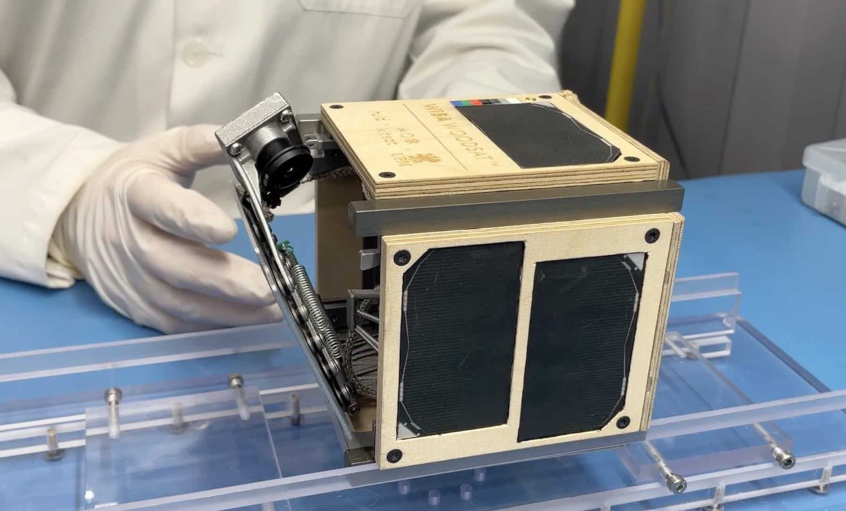
Researchers at Kyoto University, in collaboration with Sumitomo Forestry, have developed an experimental satellite named LignoSat. Set to launch to the International Space Station in September, LignoSat is a tiny cube satellite made using a traditional Japanese woodworking technique that eliminates the need for screws or glue. Scientists believe the use of wood in satellites could significantly reduce the environmental impact of satellite reentries, as traditional satellites release harmful metal particles into the atmosphere when they burn up upon reentry.
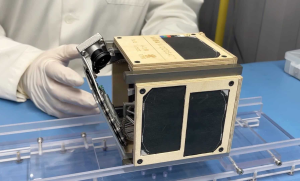
Japan builds world’s first wooden satellite
The inventive applications of wood extend far beyond traditional uses, showcasing its versatility as a sustainable, carbon-friendly, and environmentally beneficial material. From renewable energy and advanced construction materials to transparent wood and space satellites, wood is playing a critical role in shaping a sustainable future. By continuing to explore and expand the uses of wood, researchers are not only advancing technology but also promoting healthier forest ecosystems, reducing carbon footprints and paving the way for a greener planet.
These innovative applications underscore the importance of a thriving forestry sector, and it begins with policies that support working forests and ensure they remain so. After all, a robust forest products economy is essential for maintaining healthy forests that help clean our air and water, provide a mosaic of habitats for various wildlife, provide economic opportunity and enhance our quality of life.